点击关注公众号,Java干货及时送达
@Transactional注解简介
@Transactional是spring中声明式事务管理的注解配置方式,相信这个注解的作用大家都很清楚。@Transactional注解可以帮助我们把事务开启、提交或者回滚的操作,通过aop的方式进行管理。
通过@Transactional注解就能让spring为我们管理事务,免去了重复的事务管理逻辑,减少对业务代码的侵入,使我们开发人员能够专注于业务层面开发。
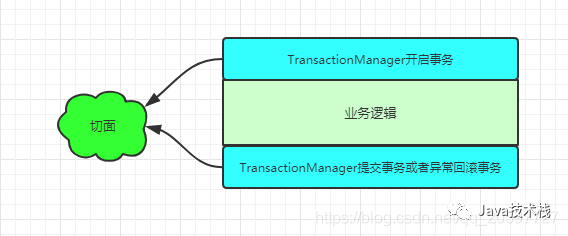
我们知道实现@Transactional原理是基于spring aop,aop又是动态代理模式的实现,通过对源码的阅读,总结出下面的步骤来了解实际中,在spring 是如何利用aop来实现@Transactional的功能的。
spring中声明式事务实现原理猜想
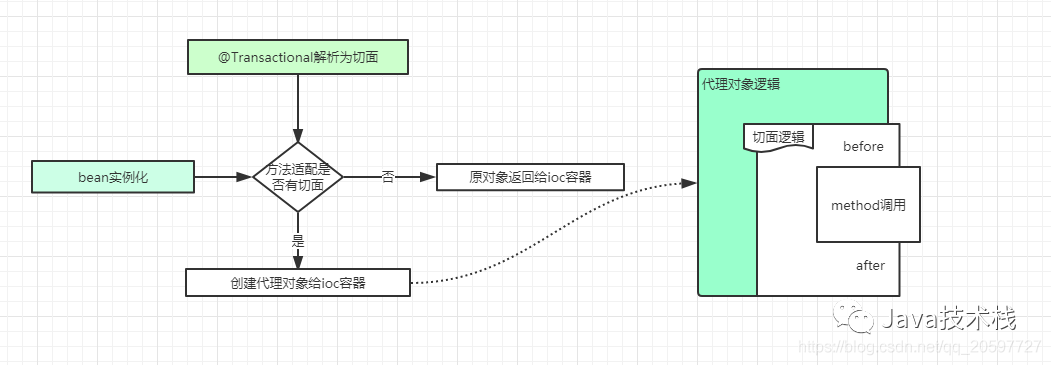
首先,对于spring中aop实现原理有了解的话,应该知道想要对一个方法进行代理的话,肯定需要定义切点。在@Transactional的实现中,同样如此,spring为我们定义了以 @Transactional 注解为植入点的切点,这样才能知道@Transactional注解标注的方法需要被代理。
有了切面定义之后,在spring的bean的初始化过程中,就需要对实例化的bean进行代理,并且生成代理对象。
生成代理对象的代理逻辑中,进行方法调用时,需要先获取切面逻辑,@Transactional注解的切面逻辑类似于@Around,在spring中是实现一种类似代理逻辑。
@Transactional作用
根据上面的原理猜想,下面简单介绍每个步骤的源码以进行验证。推荐一个 Spring Boot 基础教程及实战示例:https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice
首先是@Transactional,作用是定义代理植入点。我们知道代理对象创建的通过BeanPostProcessor的实现类AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInstantiation方法来实现个,如果需要进行代理,那么在这个方法就会返回一个代理对象给容器,同时判断植入点也是在这个方法中。
那么下面开始分析,在配置好注解驱动方式的事务管理之后,spring会在ioc容器创建一个BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例,这个实例可以看作是一个切点,在判断一个bean在初始化过程中是否需要创建代理对象,都需要验证一次BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor是否是适用这个bean的切点。如果是,就需要创建代理对象,并且把BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例注入到代理对象中。
前文我们知道在AopUtils#findAdvisorsThatCanApply中判断切面是否适用当前bean,可以在这个地方断点分析调用堆栈,AopUtils#findAdvisorsThatCanApply一致调用,最终通过以下代码判断是否适用切点。
-
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass)这里可以根据参数打上条件断点进行调试分析调用栈,targetClass就是目标class …一系列调用 -
最终
SpringTransactionAnnotationParser#parseTransactionAnnotation(java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement)
@Override public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement ae) { //这里就是分析Method是否被@Transactional注解标注,有的话,不用说BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor适配当前bean,进行代理,并且注入切点 //BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(ae, Transactional.class); if (attributes != null) { return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes); } else { return null; } }上面就是判断是否需要根据@Transactional进行代理对象创建的判断过程。@Transactional的作用一个就是标识方法需要被代理,一个就是携带事务管理需要的一些属性信息。
点击关注公众号,Java干货及时送达
动态代理逻辑实现
【aop实现原理分析】中知道,aop最终的代理对象的代理方法是
-
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept
@Override public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; Class<?> targetClass = null; Object target = null; try { if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } // May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we // "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool... target = getTarget(); if (target != null) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } //follow List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); Object retVal; // Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is, // no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target. if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly. // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know // it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot // swapping or fancy proxying. Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed(); } retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal); return retVal; } finally { if (target != null) { releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }通过分析 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass)返回的是TransactionInterceptor,利用TransactionInterceptor是如何实现代理逻辑调用的?
跟踪new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
发现最终是调用TransactionInterceptor#invoke方法,并且把CglibMethodInvocation注入到invoke方法中,从上面可以看到CglibMethodInvocation是包装了目标对象的方法调用的所有必须信息,因此,在TransactionInterceptor#invoke里面也是可以调用目标方法的,并且还可以实现类似@Around的逻辑,在目标方法调用前后继续注入一些其他逻辑,比如事务管理逻辑。
另外,Spring 系列面试题和答案全部整理好了,微信搜索Java技术栈,在后台发送:面试,可以在线阅读。
TransactionInterceptor–最终事务管理者
下面看代码。
-
TransactionInterceptor#invoke
@Override public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { // Work out the target class: may be {@code null}. // The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class // as well as the method, which may be from an interface. Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null); // Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction... return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new InvocationCallback() { @Override public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable { return invocation.proceed(); } }); }继续跟踪invokeWithinTransaction,下面的代码中其实就可以看出一些逻辑端倪,就是我们猜想的实现方式,事务管理。
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable { // If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional. final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass); final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr); final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass); if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) { // Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls. //开启事务 TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); Object retVal = null; try { // This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain. // This will normally result in a target object being invoked. //方法调用 retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { // target invocation exception //回滚事务 completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); throw ex; } finally { cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } //提交事务 commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); return retVal; } else { // It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in. try { Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, new TransactionCallback<Object>() { @Override public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) { TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); try { return invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) { // A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback. if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) ex; } else { throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex); } } else { // A normal return value: will lead to a commit. return new ThrowableHolder(ex); } } finally { cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } } }); // Check result: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow. if (result instanceof ThrowableHolder) { throw ((ThrowableHolder) result).getThrowable(); } else { return result; } } catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) { throw ex.getCause(); } } }总结
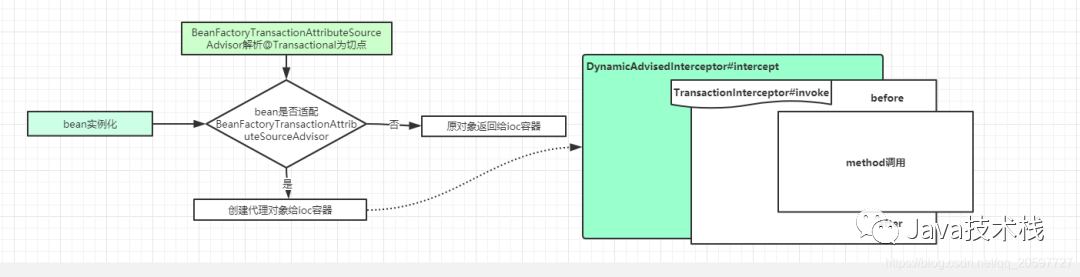
最终可以总结一下整个流程,跟开始的猜想对照。另外,关注公众号Java技术栈,在后台回复:面试,可以获取我整理的 Spring 系列面试题和答案,非常齐全。
分析源码后对照
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_20597727/article/details/84868035
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「一撸向北」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
关注Java技术栈看更多干货获取 Spring Boot 实战笔记!
热门文章
- 「12月21日」最高速度20.5M/S,2024年Free Xray Node每天更新免费机场订阅节点链接
- 「12月22日」最高速度22.8M/S,2024年Free Xray Node每天更新免费机场订阅节点链接
- 「1月2日」最高速度21.3M/S,2025年Free Xray Node每天更新免费机场订阅节点链接
- 「11月21日」最高速度19.6M/S,2024年Free Xray Node每天更新免费机场订阅节点链接
- 长沙宠物领养救助站电话 长沙宠物领养救助站电话号码
- FreeRTOS进阶之任务切换完全分析_操作系统_
- 「11月30日」最高速度20.3M/S,2024年Free Xray Node每天更新免费机场订阅节点链接
- 「11月17日」最高速度20.5M/S,2024年Free Xray Node每天更新免费机场订阅节点链接
- 2021年国考公务员考试报名时间(2022年国考公务员考试报名时间)
- 「12月27日」最高速度20.5M/S,2024年Free Xray Node每天更新免费机场订阅节点链接